Any future strategy for modern businesses must, at its heart and throughout every aspect, honor ESG. Standing for environmental, social and governance, ESG represents a measurement framework for assessing the impact of a company’s operations on its environment, from the natural world to the social and industrial communities of which it is a part.
Over the years and through different guises, ESG has evolved from a nice-to-have to a business imperative. And it will only continue to grow in importance – today, tomorrow and in the future.
The early days of environmental, social and governance standards
The early days of ESG can be traced back to the 1960s and 1970s, when socially responsible investing (SRI) began to gain popularity. SRI involves selecting investments based on a company’s social or environmental impact, as well as its financial performance.
In the 1980s, the term ‘corporate social responsibility’ (CSR) gained popularity, as companies began to recognize the importance of being responsible and transparent about their impact on society and the environment. However, it wasn’t until the 2000s that ESG became a commonly used term in the investment world.
Today, ESG factors are widely considered to be a vital part of investment analysis, as investors seek to back companies that are socially responsible and sustainable as well as financially sound.
The early days of ESG were characterized by a lack of standardization and consistency in how ESG factors were measured and evaluated. However, in recent years, there has been a push towards greater standardization and transparency in ESG reporting, as investors and stakeholders demand more information about companies’ ESG performance. Today, ESG factors are widely considered to be a vital part of investment analysis, as investors seek to back companies that are socially responsible and sustainable as well as financially sound.
In their recent report, Anatomy of an Effective ESG Program, Gartner predicts that broad-based ESG reporting requirements will be in place by 2025. They say: “Organizations must now evolve their ESG initiatives from compliance-driven efforts to strategic programs that integrate the organization’s environmental, social and governance priorities into strategic decision making and operational execution.”
Mainstream adoption
In recent years, ESG has become increasingly mainstream, with more investors, customers, and stakeholders demanding that companies prioritize sustainability and social responsibility. This has led to the rise of ESG ratings and indices, used by investors and other stakeholders to evaluate companies based on their ESG performance.
One of the main drivers has been the shift in investor preferences towards companies that demonstrate strong ESG performance. This has been driven in part by younger investors, who are more likely to consider social and environmental factors when making investment decisions. Institutional investors, such as pension funds and endowments, have also been increasing their allocation to ESG investments, further helping to push ESG investing into the mainstream.
The growing availability of ESG data and research has also helped to drive mainstream adoption. This has helped to standardize ESG metrics and make it easier for investors to evaluate companies.
Regulators have also been playing a role, introducing new elements that increase transparency and accountability.
Regulatory pressures
In some countries, regulators have started mandating ESG reporting, which is forcing companies to take ESG issues seriously. For example, the European Union’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation requires companies to disclose ESG data in their reporting.
In recent years, regulatory pressures for businesses to prioritize ESG factors have been increasing. Governments and regulatory bodies around the world are recognizing the importance of sustainability and responsible business practices, and are taking steps to encourage companies to act and operate more responsibly.
As well as mandatory reporting requirements, some governments are offering incentives for companies to adopt ESG standards, such as tax breaks or subsidies for companies that invest in renewable energy or other environmentally-friendly initiatives.
Regulators are also taking steps to penalize companies that fail to meet ESG standards, with fines or other penalties imposed on companies that violate environmental regulations or engage in unethical business practices.
Integration into business strategy
It’s clear that ESG has a critical impact on a company’s financial performance, reputation, and long-term sustainability. Unsurprisingly, more and more companies are now integrating ESG into their business strategy, from setting targets to using ESG as a lens for decision-making, considering the environmental and social impacts of their operations alongside financial considerations.
For a strong foundation, strategic planning and execution should consider:
- Goals and targets. This can include targets related to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving working conditions, or increasing diversity, equity and inclusion. By setting these targets, companies can focus their efforts on specific ESG issues and track their progress over time – after all, without meaningful measurement and reporting, impact (good or bad) cannot be proven.
- Alignment with core business activities. For example, a renewable energy company might integrate ESG factors into its product development process by focusing on developing more efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
- Listening to stakeholders. By engaging with stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees, and listening to their needs and concerns, companies can identify ESG issues that are important to them and develop strategies to address these issues, offering first-mover competitive advantage and increasingly loyalty.
- Making ESG part of company culture. From training employees on ESG issues to incorporating ESG considerations into performance evaluations and compensation packages, weaving ESG into the culture of your organization is key. From an executive sponsorship point of view – as with all projects – it’s imperative that this aspect of the company culture comes from the top. Establishing committees or task forces to oversee ESG initiatives is a highly effective way of upholding sustainable business principles, as well as helping senior leadership check in across the business.
Impact on performance
As ESG becomes more integrated into business strategy, it is, of course, having an impact on business performance. Companies that prioritize ESG are more resilient, have lower risk profiles, and are better able to attract and retain customers, investors and talent. This has led to growing recognition that ESG is not just a moral imperative, but also makes good business sense.
Companies that prioritize ESG are more resilient, have lower risk profiles, and are better able to attract and retain customers, investors and talent. This has led to growing recognition that ESG is not just a moral imperative, but also makes good business sense.
Studies have shown that companies with strong ESG performance are more likely to outperform their peers in terms of financial performance over the long term. This is because ESG factors can impact a company’s revenue growth, cost management, and risk management, which can all have a positive impact on financial performance.
When it comes to brand reputation, socially and environmentally-conscious companies are viewed more positively by customers, employees, and other stakeholders, in turn having a positive effect on revenues, customer retention rates, and employee recruitment and retention.
Last but not least, ESG reduces business risks. By transforming their strategy, operations and culture to embed circular principles that drastically reduce waste and greenhouse emissions, for example, companies can reduce their risk exposure relating to environmental and social issues, as well as governance concerns. In turn, this protects the company’s reputation, avoids legal and regulatory penalties, and reduces the likelihood and impact of costly incidents such as environmental disasters or supply chain disruptions.
What the future holds
The future of ESG will continue to evolve, as companies, investors and regulators increasingly recognize the importance of sustainability and responsible business practices. Here are some potential trends and developments that could shape the future of ESG:
- Increasing emphasis on social factors: While environmental and governance factors have traditionally received the most attention in ESG, there is likely to be a growing emphasis on social factors such as diversity, equity and inclusion. To position for success, prioritize social factors that attract and retain employees, build customer loyalty, and improve reputation overall.
- Greater standardization and transparency: There will be an increase in standardization and transparency in ESG reporting, as investors and other stakeholders seek to ensure that ESG data is comparable, reliable and accurate. This is likely to include the development of common ESG reporting frameworks, or the establishment of ESG reporting standards by regulatory bodies. Getting ahead of regulation will pay dividends in the long run.
- Increased focus on climate change: Climate change will remain a key area of focus, as the global community seeks to address the growing threat of the climate emergency. Recently, PwC reported that most global CEOs expect some degree of impact from climate change in the next 12 months, and that the area most impacted by climate risk will be cost profiles and supply chains. The report goes on: “Moving with the right pace and priority to mitigate climate risks, generate opportunities and decarbonize are enormous strategic challenges… Experience shows it’s crucial for leaders to break the climate challenge down into manageable chunks.”
The future you want
In their report showcasing the elements of an effective ESG program, Gartner calls out four areas that companies should develop in order to establish a mature, strategy-driven framework.
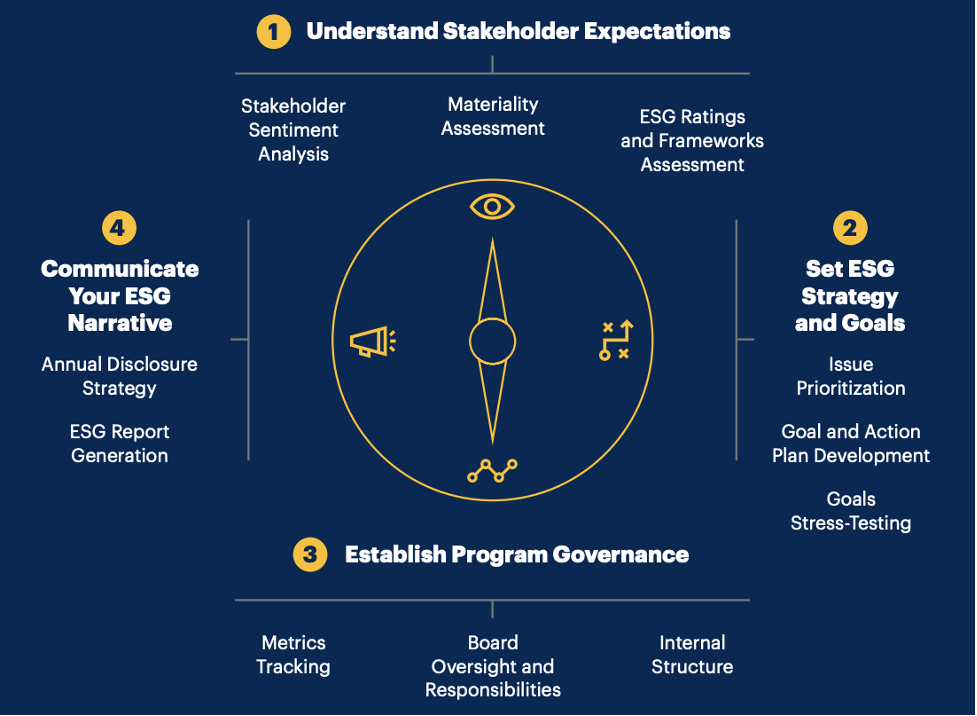
Figure: Four elements of an effective ESG program (source: Gartner)
Companies that are mature in ESG practices set priorities through a robust process, looking at long-term business needs and environmental constraints, in addition to commercial opportunity, organizational capability, and stakeholder sentiment.
By integrating these priorities into strategic decision-making and operational execution, companies that embrace this approach will win out. And the time to act is now.
And by integrating these environmental, social and governance priorities into strategic decision-making and operational execution, companies that embrace this approach will win out.
As the report makes quite clear, the time to act is now: “Organizations must prepare now and have a long-term plan to meet increasing ESG expectations by continuously honing their ESG programs using the four key components: stakeholder expectations, goals, governance and narrative. The prize for organizations that act now will be stronger engagement of ESG-oriented customers, investors and talent, and a more resilient, sustainable company.” What are you waiting for?